Sidebar

Conversation starters, celebrity health reveals, healthy living hacks and medical cautions: Here's what you missed in Fox News Health this week
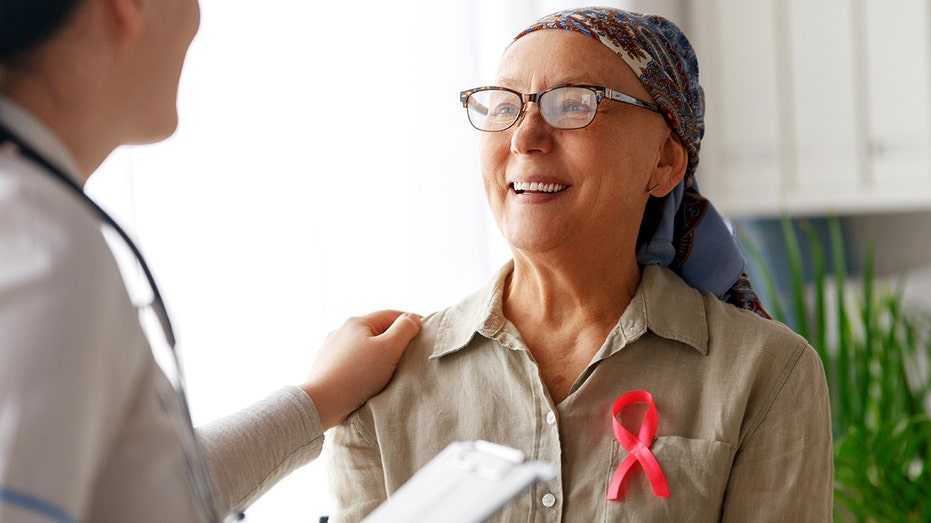
Cancer survival in the U.S. has climbed to 70%, reflecting major advances in treatment, early detection and personalized care, new data show.
Health experts weigh in on alcohol decisions after Dry January, offering guidance on finding balance between social drinking and potential health risks.
Research shows introducing peanuts during infancy cuts allergy risk, while eggs now surpass peanuts as the most common food allergen in children.
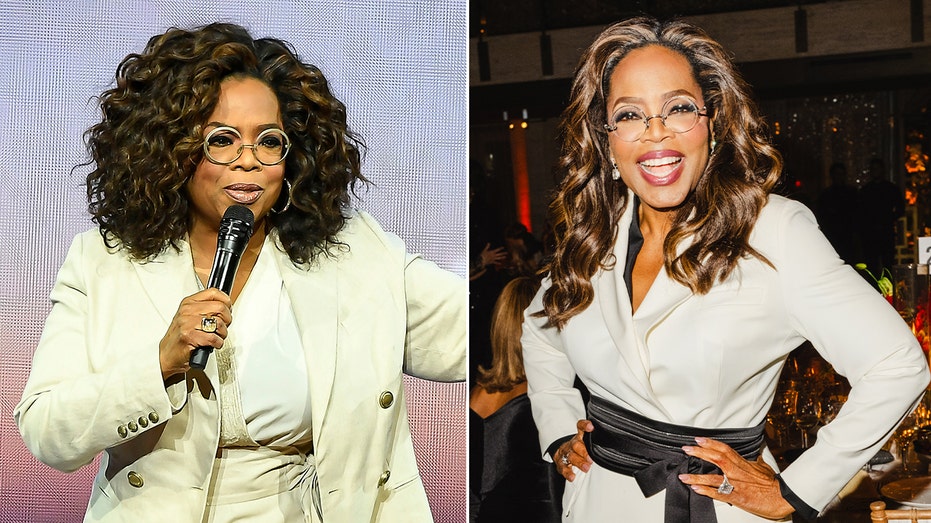
Oprah Winfrey discusses GLP-1 weight-loss medications and obesity as a disease, challenging long-held misconceptions about willpower and food addiction.
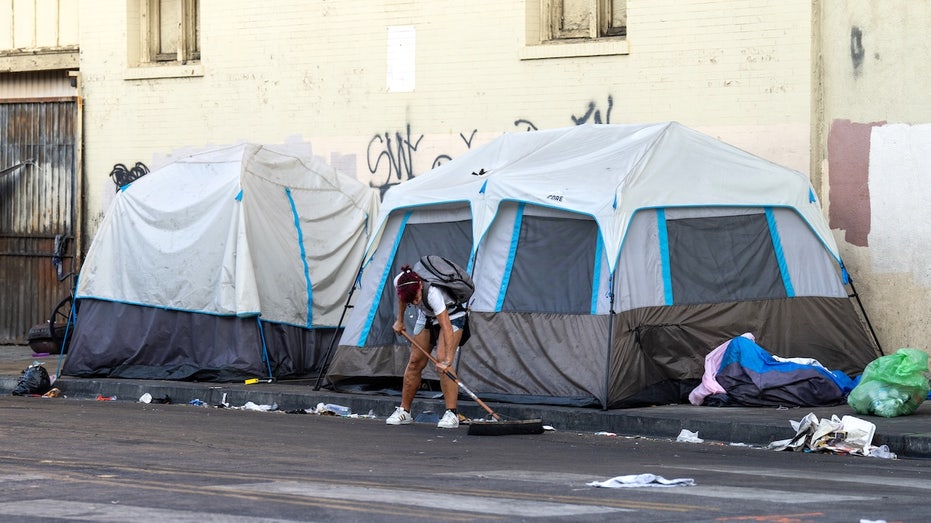
Berkeley declares a health emergency after a leptospirosis outbreak forced homeless encampment evacuations. Multiple rats and dogs were infected with the disease.
Nutrition experts support the return of whole milk to schools, citing brain development benefits. Studies have linked higher milk fat to lower child obesity.
Experts say forcing a 6 a.m. wake-up isn’t healthy for everyone. Your chronotype affects sleep quality, mood and health more than waking early.
Scientists discover microgravity in space could help fight drug-resistant superbugs by creating unique viral mutations, according to a new study.
Updated dietary guidelines shift focus to whole foods away from refined grains, with nutrition experts weighing in on saturated fat and protein limits.
Canadian researchers say a blood test measuring immune response to gut bacteria could help predict Crohn’s disease years before diagnosis.
A review of recent studies suggests exercise may treat depression as effectively as therapy or antidepressants, offering an accessible mental health treatment option.
RFK Jr. reshaped CDC's vaccine panel with new appointees, sparking debate over childhood immunization policy changes and vaccine safety recommendations.
A Stanford AI model trained on nearly 600,000 hours of sleep data can assess future risk for dementia, heart disease and more using one night of sleep, researchers say.